How to clear swap memory in Linux
How to clear swap memory in Linux

Photo by Kaboompics .com from Pexels
Swap memory is usually a "set it and forget it" type of affair. Most enterprise environments have swap built into the systems, and these memory caches are not manipulated unless there is an apparent lack of memory available or if a server crashes due to the OOM killer (out of memory) error. However, there is a niche situation that can cause an administrator to need to clear the system swap manually. If that is the situation that you find yourself in, you’ve come to the right place. This article is a discussion about this situation and the solution required.
Feeling Swappy?
Occasionally, a system uses a high percentage of swap memory even when there is RAM available for use. The culprit here is the ‘swappiness’ of the system. Yep, you read that right...swappiness. So now that you know the lingo, you're ready to explore what it means. Swappiness refers to the kernel parameter responsible for how much and how often that the system moves data from RAM to swap memory.
The default value for swappiness is 60; however, you can manually set it anywhere between 0-100. Small values cause little swapping to occur, whereas high values can cause very aggressive swapping. A value of zero causes no swapping at all to occur, so if you want to minimize swapping to its lowest possible value without turning it off, you should set it to at least one.
[ Free download: Advanced Linux commands cheat sheet. ]
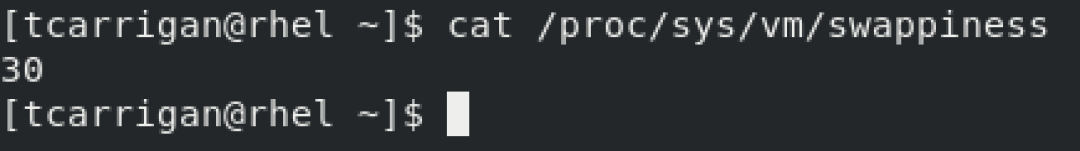
If you wanted to change up the swappiness of your system, the procedure is very straight-forward. You can check your current swappiness setting by running the following command:
$ cat /proc/sys/vm/swappinessIt should look something like this:
Now, you can see that my system has a swappiness value of 30. To alter the value, you want to use the following:
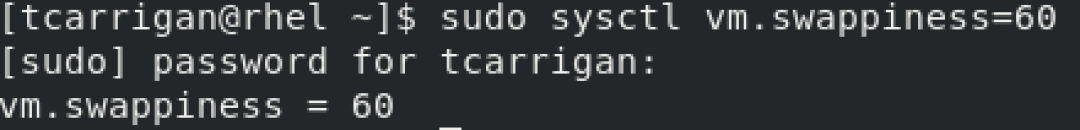
$ sudo sysctl vm.swappiness=x
(where x is the swap value you wish to set)To verify the value that you set, simply cat the swappiness file that you looked at earlier to find out the original value. Easy day. Now that you understand the underlying parameters that control the swap behavior on our system, you're ready to learn how to clear that memory, should the situation arise. For the first time in your terminal life, things are going to be easy here.
To clear the swap memory on your system, you simply need to cycle off the swap. This moves all data from swap memory back into RAM. It also means that you need to be sure you have the RAM to support this operation. An easy way to do this is to run 'free -m' to see what is being used in swap and in RAM. Once you power it off, you can wait an arbitrary amount of time (30 sec or so) to give the operation time to complete, then power the swap back on. This clears the swap memory cache and re-enables it. Here are all of the commands you'll need!
Check space: # free -m
Disable swap: # swapoff -a
Wait approx 30 sec
(use free -m to see the amount of swap used/available decrease over time)
Enable swap: # swapon -a Hopefully, this quick tip helps you clear your system swap memory if you ever find yourself in need of just such a fix.
For more information on swap space see my article outlining the basics here.